P12. Texts
Projects that support multi-language texts can be found in New Project Examples (Fig. 1) and can serve as a starting point for a project that requires the use of multiple languages.
Multi-language is currently supported only in EEZ-GUI and Dashboard projects.
P12.1. Texts panel
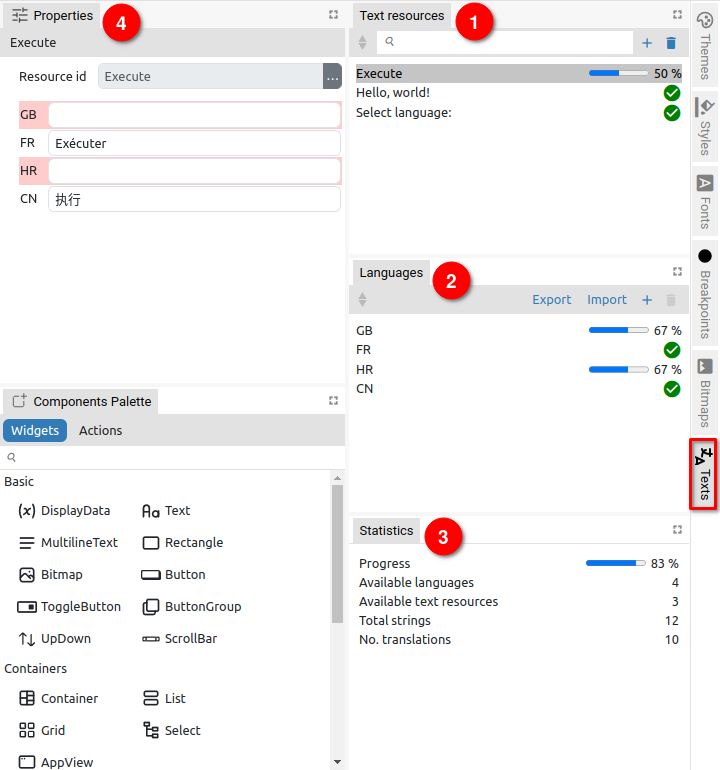
Fig. 2 shows the Texts panel for multilingual text editing, which consists of the following three tabs: Text resources (1), Languages (2) and Statistics (3).
|
|
|
Text resources contains a list of IDs of all texts that are multilingual. For each Resource ID there should be a translation for all defined Languages.
The content of the texts for all defined languages can be seen in Properties (4).
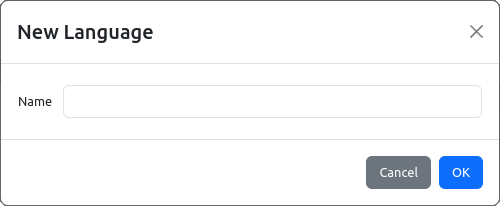
There is no limit to the number of languages and text resources in the project. When adding a new Language, a dialog will open as shown in Fig. 4, and for adding a new multilingual Text resource, a dialog opens as shown in Fig. 5.
|
|
|
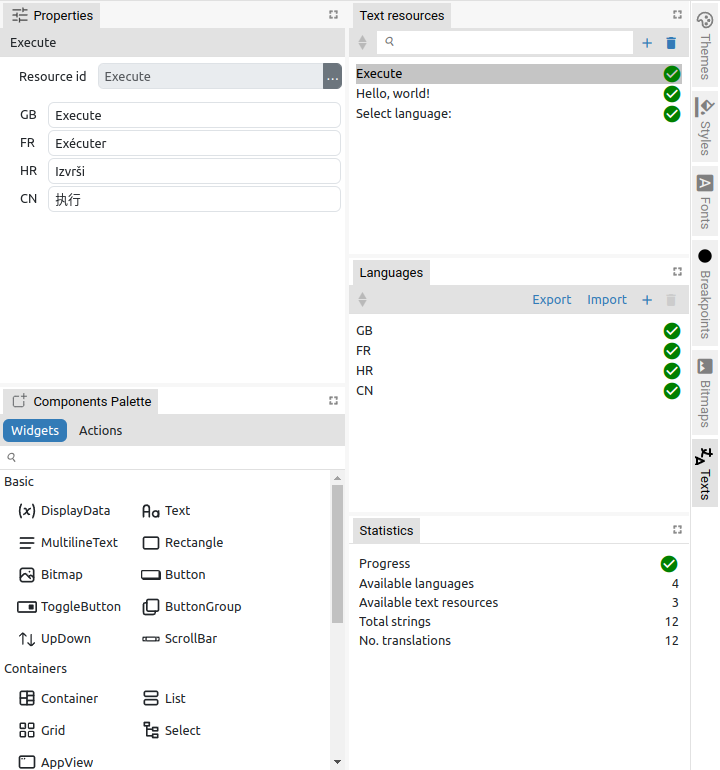
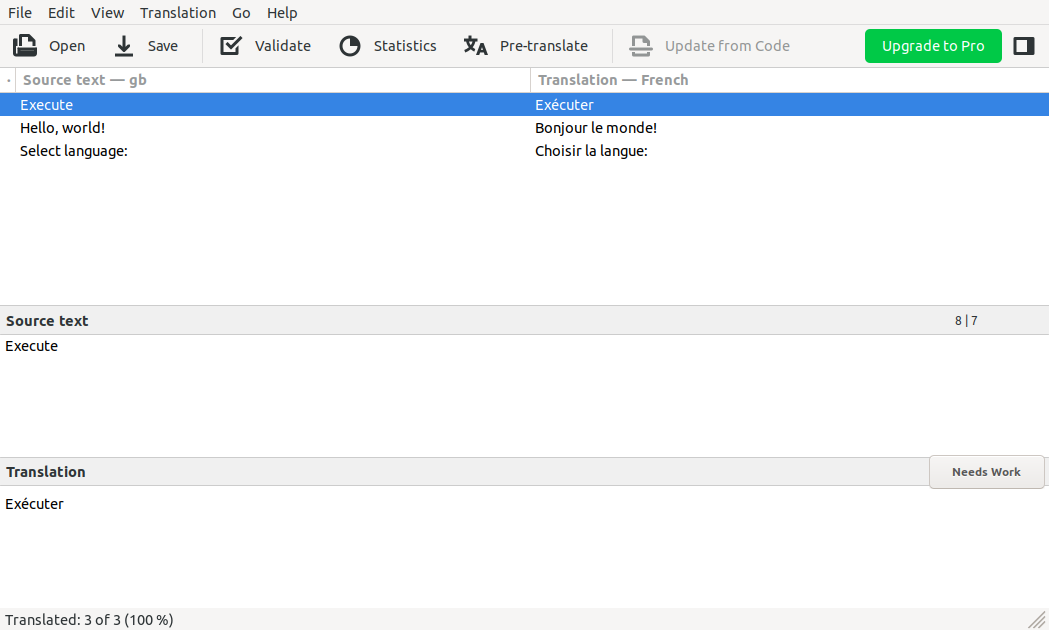
The completeness of the translation can be easily checked thanks to the progress bars for each Resource ID and Language. The overall translation statistics are displayed in the Statistics tab (3). Fig. 3 shows an example when all texts are translated.
The SelectLanguage action is used at runtime to select the active language.
There are two methods for using localized text in expressions:
- Using the special literal T"<text resource ID>". For example T"Hello, world!" where "Hello, world!" one of the IDs in the Text Resources tab.
- Using the function Flow.translate("<text resource ID>"). For example, Flow.translate("Hello, world!")
Since it is simpler, it is recommended to use the first method.
If there is currently no translation for a language, then the text resource ID itself will be used, so it is convenient for that ID to be he same as the translation for one of the languages, for example in English.
P12.2. XLIFF Import/export
XLIFF (XML Localization Interchange File Format) is an XML-based format created to standardize the way localizable data are passed between and among tools during a localization process and a common format for CAT (Computer-Aided Translation) tool exchange.
By using this format, it is possible for a professional translator to prepare translations in the tool with which he/she is familiar and deliver the translations to the developer, who will insert them into the EEZ Studio project.
Options for Import and Export text resources in XLIFF format can be found in the Language panel.
|
|
|
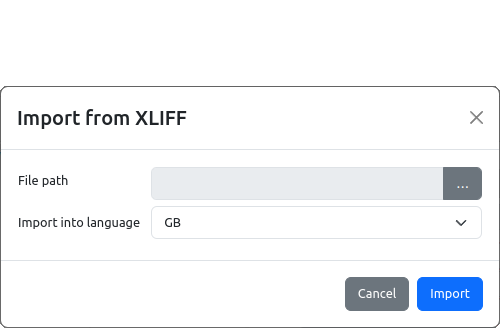
During import, a dialog opens as shown in Fig. 6 where you have to select the File path to XLIFF file and the Language into which the text strings will be imported (combo box with a list of all defined languages).
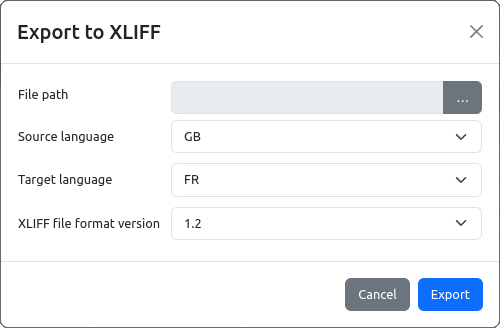
When exporting (Fig. 7), the Source language and Target language should be defined, as well as the XLIFF file format version (1.2 or 2.0 depending on what the translation tool supports). In Fig. 8 shows the exported XLIFF file in the Poedit application (Source language is GB, Target language is FR).